External female reproductive system :-
•External genitals are the accesory structure of female that are
external to the vagina and it's occupy large part of female perineum.
Perineum:- A surface or region in both female and male between the pubic symphysis and coccyx.
•External genitals are synonyms to vulva or pudendum.

|
| Fig 1.external genitals |
Parts and functions of external genitals:-
Vulva or pudendum:-
•The vulva or pudendum is the outer part of the female genitals in
perineum.
•In Latin word vulva means wrapper or covering.
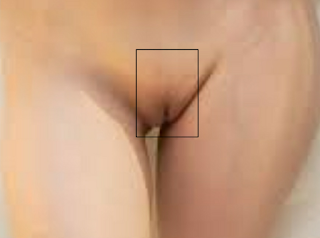
|
| Fig 2.Vulva |
Boundaries of vulva:-
- Anterior :- mons pubis
- Laterally :- labia majora
- Posteriorly:- perineum
Functions of vulva:-
•The main function of
vulva
is protection of internal organs of female reproductive system.
Parts and functions of vulva:-
1.Mons pubis :-
mons pubis is also known as mons veneris mons pubis is a pad of subcutaneous adipose connective tissue and it is situated in the anterio-posterior to pubic symphysis .
•After puberty(Average age 11 but some time the process can take up to 4 year so the age may be 8 to 14 year) it is covered by coarse
(thicker) hair in
escutcheon pattern(triangular
base directed upward) in third sign of
puberty pubarche.
➡Functions of mons pubis:-
-
protection of pubis and sexual arousal.
➡What is cause of large mons pubis:-
•the cause of large mons pubis may be simple weight gain, hormonal factors and even genetic deposition
•It is rare to find an obese woman or man who does not store excess fat in the pubic area.
2.Labia majora:-
Labia majora is also known as larger outer
lip of vulva
it is thick elevated fold of skin.
•They are composed of skin,
fibrous tissue, fat & large number of sebaceous gland
(but no hair follicle).
•It is homologous(similar in fundamental structure and in origin but not necessarily in
function) to scrotum in the male
➡Functions of labia majora :- protection of inner structure and sexual arousal.
➡colour of labia majora:-
The labia majora also may change in color. In adults, the color can range from light pink to dark brown-red or black.
•
Many light-skinned women have brown or purplish labia majora
3.Labia minora :-
labia minora is also known as small inner lip of
vulva.
There are two thin elevated folds of skin without fat.
- Anteriorly it divided and enclosed by clitoris.
- Posteriorly it makes thin skin folds known as fourchette.

|
| Fig 5.labia minora |
- Labia minora is homologous to penile urethra and parts of the penis in male.
- It is made up of erectile connective tissue and containing numerous sebaceous gland.
➡location of labia minora:--labia minora is located inside the labia majora.
➡Development of labia minora:- Development of labia minora occurs at period of third month of pregnancy from urogenital folds
➡Functions of labia minora:-
•protection of vagina.
4.Clitoris:-
clitoris
is a small cylindrical erectile body and consist two small cylindrical
erectile tissue
Corpora and cavernosa.
•Erectile tissue means spongy tissue, the space filled
with blood that cause it's harden and expand
•Clitoris is homologous to penis in the male and
is is attached to the under surface to the pubic symphysis by the
suspensory ligament.
➡Location of clitoris:-
•Clitoris is situated anteriorly of vulva
➡Length of clitoris:-
•The length of clitoris
is about 1.5cm to 2cm.
➡Functions of clitoris:-
•To give sexual arousal and pleasure during intercorse.
➡Enlarged clitoris-
•In the conditions of sexual excitement or arousal the flow of blood in clitoris is more than normal conditions due to the blood filled the clitoris are large in their size but after orgasm the blood are normal and also clitoris size
5.Vestibule :-
Vestibule
is the inner portion of vulva. It is a area that is enclosed by labia
minora
➡Shape of vestibule :-
•Vestibule is a almond-shaped (triangular) space.
➡Boundaries of vestibule :-
- Anteriorly :- Clitoris
- Posteriorly :- Fourchette
- Either side :- labia minora
➡Opening of vestibule :-
•There are four opening in the vestibule.
- Anteriorly :- urethra
- Mid portion :- vaginal orifice
- Lateral side :- bartholin gland
- "" "" "" "" "" :- skenes gland
6. Vaginal orifice :-
The vaginal orifice
lies in the posterior end of the vestibule. It is completely closed by
hymen
-
Hymen :- A thin layer of mucous membrane that is partially cover opening
of vaginal in virgin female during sexual intercourse and child
birth it may rupture. It is not present in some women Like:-
Athletic girl, sports women and after coital Act.
➡Relations of vaginal orifice :-
- Anterior :- Bladder or urethra
- Posterior :- Rectum and anal canal
7.Bartholin gland :-
- Bartholin gland first described by casper bartholin (1677) .
- It is two small pea sized compound mucous glands and it is greater vestibule gland.
- The duct is lined by columnar epithelium but near it's opening by stratified squamous epithelium
- Bartholin gland carry the secretions of alkaline that is suitable for sperm activities
- It is homologous to bulb of penis.
➡Colour of bartholin gland :-
The colour of bartholin duct is yellowish white.

|
| Fig. 8 Bartholin gland |
➡Location of bartholin gland :-
The bartholin gland ia located in each lateral wall of the vestibule of the vagina, near the vaginal opening at the base of the labia majora.
➡Functions of bartholin gland:-
- Help in easy fertilization
- Lubricant the vagina
- Secretions increase with sexual excitement
8. Skene's gland :-
- SKene's gland is lesser vestibule gland and largest para urethral.
- Two skene's duct open in the vestibule on either side of the external urethral meatus (female ejaculation)
- It is homologous to prostate in male
➡Purpose of skene's gland :-
•The purpose of skene's gland is secrete mucous containing fluid substance these substance help in lubricant of urethra.

|
| Fig. 9 Skene's gland |
9.Vestibule bulbs :-
- These are bilateral elongated masses of erectile tissue beneath the mucous membrane of the vestibule and infront of the bartholin gland.
- They are homologous to the male corus spongiosum.
I hope you like our article on External female reproductive system
and its parts and function if you like and have any query about this article
please tell us on comment box and is helpful for you I suggest YouTube video
that is given above for fully understand External female reproductive system
and its parts and function,so please watch it now and share your
friends.
Thank you.






2 Comments
nice sir tnx
ReplyDeleteTnx dear
ReplyDeletePlease don't enter any spam link in comment box